Economic risks and geopolitical tensions have deeply affected the global economy throughout 2023 and continue to cast a shadow over the globe into 2024. Yet, despite these ongoing challenges, Southeast Asia is anticipated to experience encouraging developments in 2024, becoming a bright spot in the global economic landscape.
• Optimistic Growth Forecast
After a tumultuous 2023, WorldBox Business Intelligence, a financial and business information analysis service covering over 50 million companies worldwide, has recently issued its economic outlook forecast for Southeast Asia in 2024, with both challenges and optimistic signs. Even amidst gloomy predictions for the global economy, Southeast Asia is expected to maintain its status as “one of the most dynamic regions in the world”. According to the Asian Development Bank (ADB) in its “December 2023 Asian Economic Outlook”, ASEAN countries are forecasted to achieve a growth rate of 4.3% in 2023. In the broader context of the global economy, where some advanced economies are at risk of recession, this growth rate stands out as relatively high.
Moving into 2024, ADB forecasts ASEAN’s growth to reach 4.7%. The Philippines is projected to have the highest growth rate in the ASEAN region at 6.2%, followed by Vietnam at 6%. Meanwhile, Indonesia, the largest economy in the region, is forecasted to grow at 5%, with Singapore having the lowest forecasted growth rate at 2.5%.
Additionally, several trade agreements, including the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), are expected to create strong platforms for expanding trade and investment in the region. Southeast Asian countries will continue to be attractive destinations for foreign direct investment (FDI). Increasing FDI and the continuing shift in production supply chains will leverage Southeast Asia in the global trade recovery process. Public investment and consumer spending are also seen as factors of economic growth for ASEAN countries, especially international tourism expenditure. Furthermore, the recovery in the international electronic and technological trade will further improve the growth prospects of countries in the region.
• Tourism Boosting Economic Growth in Southeast Asia

Tourism is expected to be a driving force of economic growth in Southeast Asian countries in 2024. According to the Pacific Asia Travel Association (PATA), the outlook for the beginning of 2024 appears promising, with travel restrictions lifted and tourist destinations reopening across the Asia-Pacific region. The implementation of visa exemption policies has made some Southeast Asian countries top choices for tourists, particularly for Chinese tourists. On the LY.com online travel platform, during the recent 8-day Lunar New Year holiday, international bookings, especially from Chinese tourists, for Malaysia and Singapore increased ninefold compared to the previous year. Similarly, research data from Agoda indicates that Vietnam has become a popular tourist destination for Chinese travelers at the start of 2024. Specifically, the search volume from China to Vietnam during the recent Tet holiday almost returned to pre-pandemic levels.
In addition to visa exemption policies, the increase in low-cost flights offered by airlines is also stimulating tourism demand. According to ForwardKeys, for global tourists traveling to the Asia-Pacific region from December 23, 2023 to January 6, 2024, VietJet Air, Air Asia, and Thai Air Asia exceeded their 2019 seat capacity by 105%, 6%, and 27%, respectively. The affordable cost of traveling is also considered an attractive factor for tourists visiting Southeast Asian countries.
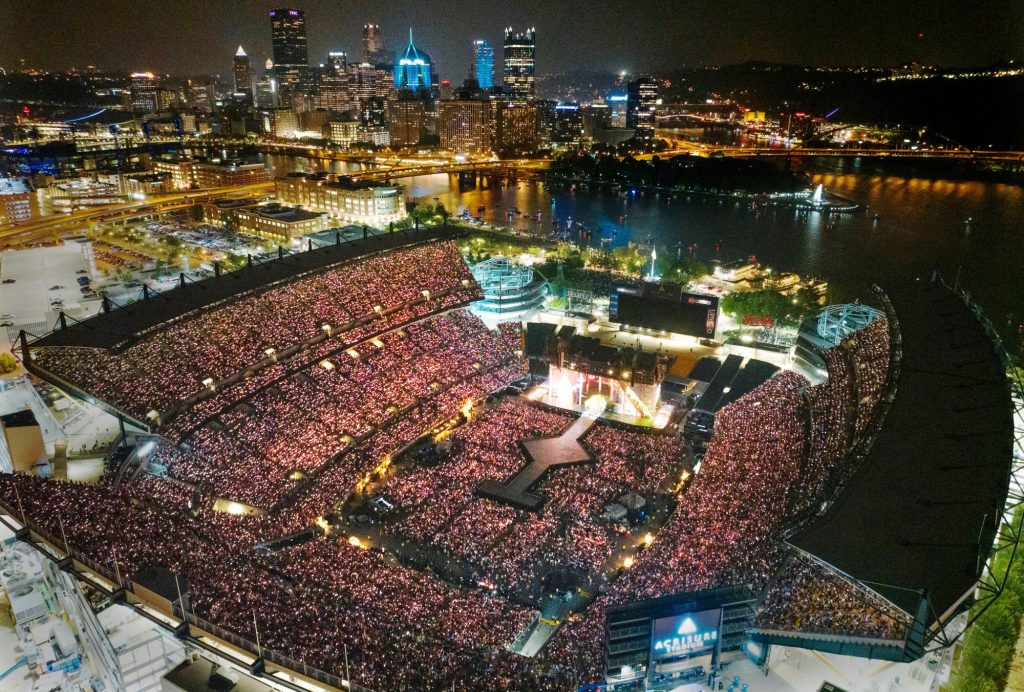
Following the resoundingly successful music event featuring singer Taylor Swift in Singapore, a new tourism trend has emerged, garnering the interest of governments across Southeast Asian countries. High-profile music shows by popular idols not only evoke strong emotions but also generate tangible economic benefits through record-breaking numbers. The Eras Tour music event in Singapore, according to economic experts, generated approximately $260 to $371 million in tourism revenue. Music idol performances have an immediate effect of attracting fans to the country, benefiting the local economy and tourism sector. This also creates opportunities for other related sectors such as hotels, nightlife tourism, food and beverage (F&B), etc., to develop.
• Attractive Destination for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
According to many economic experts, Southeast Asia is expected to become an increasingly important destination for foreign direct investment (FDI) as multinational companies diversify supply chains to leverage the region’s growing competitive advantages. What makes ASEAN attractive to foreign investors stems from factors such as abundant labor force, young population, and safe investment environment due to the region’s distance from geopolitical conflicts like Russia-Ukraine or Hamas-Israel. Most importantly, what truly draw FDI to the region are the many attractive incentives that Southeast Asian countries offer to foreign investors. Governments in ASEAN put great importance on attracting investment by focusing on important areas such as energy transition, digital economy, wholesale and retail trade.
Green economic development and digital transformation are two focal points in the development strategy of Southeast Asian countries in 2024. Recognizing the importance of attracting FDI for economic development, Southeast Asian countries have updated and developed many favorable policy frameworks, aiming to build a stable business environment, ensure a fair and efficient legal system, and promote equal treatment for all investors. For instance, in the green economy sector, many countries have offered incentives, subsidies, and reduced consumption taxes to encourage FDI in electric vehicle (EV) production. In 2021, Cambodia reduced import taxes on electric cars from 30% to 10%, 50% lower than their current rate applied on ICE (Internal Combustion Engine) cars. Indonesia has implemented programs to reduce electricity prices for charging stations, while encouraging investment in high-value nickel products by reducing tax incentives for lower-value ones. Malaysia has provided many incentives to encourage the establishing of electric charging stations and simplified approval procedures. Myanmar, meanwhile, has exempted income tax, special commodity taxes and other domestic taxes for battery-powered electric vehicles to attract more foreign investment in this sector.

In the digital transformation field, Southeast Asia is known for its vibrant mobile market and rapid digitalization, poised for significant growth in smartphone users and internet penetration rates. Internet penetration rates in Southeast Asia have surged, reaching over 70% of the region population by early 2023. This growth is driven by the widespread use of smartphones, along with improvements in internet infrastructure. With a projected GDP growth rate of 5% in 2024, Southeast Asia is set to become an attractive investment destination. Technology investment will become even more important in the coming years, fostering a desirable environment for breakthrough of startup companies, and reinforcing the digital ecosystem of Southeast Asia.

Overall, most ASEAN countries will have another year of strong growth despite global challenges. Additionally, economic experts predict that growth will accelerate in the second half of the year due to looser monetary policies implemented by advanced economies. This will provide a basis for confidence and hope for a brighter global economy in 2024.

Head of Market Intelligence, PeopleWise Vietnam.
As a Ph.D. Student, Research in Economics, Tuyen Le provides market insights, industry trends, and research on labor and workforce effectiveness. Through her research and analysis, she helps business leaders identify potential risks and threats to their businesses and industries, allowing them to take preemptive measures and invest with calculated risks and outcomes.

