Since the beginning of the year, the global economy has faced numerous shocks, including escalating political tensions, persistent high inflation, and continued tight monetary policy. However, economies have remained resilient, demonstrating the adaptability of nations in the face of a challenging global landscape. International organizations have successively raised their economic growth forecasts for the year, although significant risks remain.
- A More Optimistic Global Economic Outlook for 2024 Compared to Previous Forecasts
According to the General Statistics Office report, as of the end of June 2024, international organizations have adopted a more optimistic outlook on global economic growth for 2024 compared to previous forecasts. Specifically, the World Bank (WB) forecasts global growth in 2024 to reach 2.6% (an increase of 0.2 percentage points compared to the January 2024 forecast). Fitch Ratings (FR) predicts global economic growth in 2024 to reach 2.6%, a 0.2 percentage point increase compared to its March 2024 forecast. The United Nations (UN) estimates global economic growth at 2.7% in 2024 (an increase of 0.3 percentage points compared to the January 2024 forecast). The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) forecasts global GDP growth in 2024 to reach 3.1% (an increase of 0.2 percentage points compared to the February 2024 forecast). The European Union (EU) forecasts global economic growth of 3.2% in 2024 (an increase of 0.1 percentage points compared to 2023 growth). The International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimates global economic growth at 3.2% in 2024, an upward revision of 0.1 percentage points from its January 2024 forecast.
Figure 1. Assessment of Global Growth in 2023 and Forecasts for 2024 by International Organizations
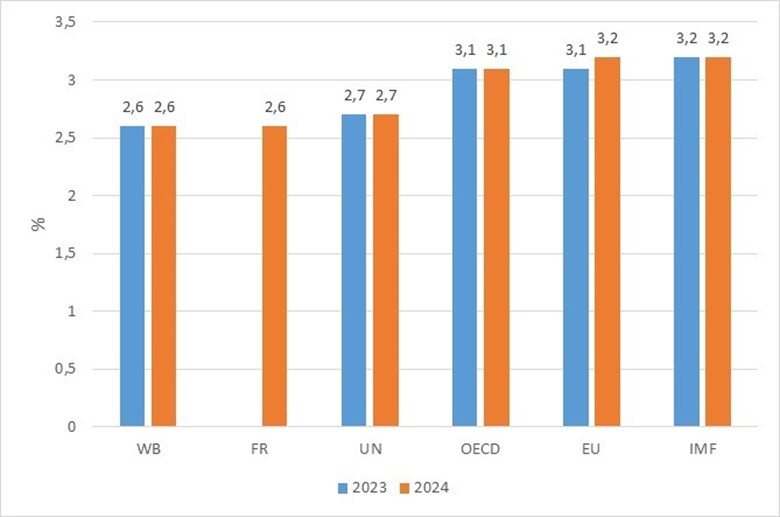
Source: WB, FR, UN, OECD, EU and IMF
The figure above shows that most international organizations (WB, FR, UN, OECD and IMF) estimate that the global GDP growth rate in 2024 will be similar to the 2023 growth rate, reaching between 2.6% and 3.2%. The EU holds a more optimistic view, forecasting global growth in 2024 to reach 3.2%, 0.1 percentage points higher than the 2023 growth rate and also the highest among the forecasts.
The IMF attributes this optimism to the increase in global activity and world trade at the beginning of the year. These activities are driven by strong exports from Asia, particularly in the technology sector, which directly contributed to a significant increase in international trade.
China and India are expected to be the strongest growing economies in Asia in the second half of 2024. China’s 2024 economic growth forecast has been revised upward to 5% due to a recovery in private consumption and strong exports. China’s exports in the remaining half of the year are expected to be dominated by electronics, transportation and automobiles (including electric vehicles). Not just China, but India is also expected to grow strongly in the second half of 2024. The growth forecast for 2024 for India has been slightly increased by 0.2%, reaching 7%. This is due to the completion of the reassessment of India’s 2023 economic growth, with results better than initially estimated. The Eurozone is also showing signs of recovery.
- Southeast Asia to Remain “One of the Most Dynamic Regions in the World”
After a turbulent 2023, WorldBox Business Intelligence, a financial and business information analysis service covering over 50 million companies worldwide, recently released its economic outlook for Southeast Asia in 2024, highlighting both challenges and optimistic signals. Despite the gloomy predictions for the global economy, Southeast Asia is expected to remain “one of the most dynamic regions in the world”.
Entering 2024, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) forecasts ASEAN growth in 2024 to reach 4.7%. According to the financial institution, the Philippines is projected to have the highest growth rate in the ASEAN region in 2024 at 6.2%, followed by Vietnam at 6%. Indonesia, the largest economy in ASEAN by GDP, is projected to grow at 5%, while Singapore is expected to have the lowest growth rate next year at 2.5%.
In addition, several trade agreements, including the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), are expected to create a solid foundation for expanding trade and investment within the region. Southeast Asian countries will remain attractive destinations for foreign direct investment (FDI). Increased FDI and the shift in production supply chains will provide leverage for Southeast Asia in the global trade recovery process.
Public investment and consumer spending are also considered factors driving growth in ASEAN countries, especially spending by international tourists visiting each country. Additionally, the recovery in exports of electronics and technology is expected to further improve the growth prospects of countries in the region.

RCEP is expected to create a solid foundation for expanding trade and investment.
- Vietnam’s Economic Picture in the First Half of 2024
With the positive global outlook in the first half of the year, international organizations and experts are optimistic about the strong growth of the Vietnamese economy in the final months of 2024. According to the General Statistics Office, the Vietnamese economy grew by 6.42% in the first half of the year, estimated to reach 6.93% in the second quarter. The socio-economic situation in the first six months of 2024 maintained a positive trend, with each quarter performing better than the previous one. Various sectors and fields achieved significant results, creating momentum for growth in the following quarters.
This strong growth is attributed to changes in state policies. The government has focused on implementing reforms and perfecting institutions, removing barriers to business and investment, and creating a transparent and open environment that is considered by foreign investors to be welcoming and friendly. As a result, Vietnam’s macroeconomic stability was maintained in the first half of 2024, exports continued to grow strongly (14.5%), resulting in a large trade surplus of 11.63 billion USD, contributing to ensuring the balance of payments.
The service and tourism sectors recovered strongly, public debt and the state budget deficit were well controlled, well below the limits. Notably, foreign direct investment attraction reached nearly 15.2 billion USD, an increase of 13.1% compared to the same period in 2023, indicating that foreign investors continue to have confidence in the Vietnamese investment environment. In addition, factors such as the recovery of demand in the semiconductor industry, stable growth in China and Southeast Asia, and the potential for easing monetary policy by major central banks are all supportive factors for Vietnam’s economic prospects.
Recovery of the semiconductor industry is an important factor for Vietnam’s economic prospects.
The global macroeconomic landscape in the first half of 2024 presents a complex picture, intertwined with persistent uncertainties and emerging positive prospects. While geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions continue to pose challenges, bright spots of resilience and potential growth momentum are gradually emerging. According to the IMF’s latest forecast, Vietnam’s economic growth in 2024, despite facing many challenges, will generally remain above 6%, and inflation will be maintained close to the target of 4.5%. The Asian Development Bank (ADB) shares a similar view, maintaining its growth forecast for Vietnam’s economy in 2024 at 6% and stable inflation at 4%. The economic achievements in the first half of 2024 have paved the way for expectations of even better growth in the final months of the year. Both domestic and international economic experts believe that Vietnam’s economy will “continue to recover” in the second half of 2024.

Head of Market Intelligence, PeopleWise Vietnam.
As a Ph.D. Student, Research in Economics, Tuyen Le provides market insights, industry trends, and research on labor and workforce effectiveness. Through her research and analysis, she helps business leaders identify potential risks and threats to their businesses and industries, allowing them to take preemptive measures and invest with calculated risks and outcomes.

